Shopping Cart
There are no more items in your cart
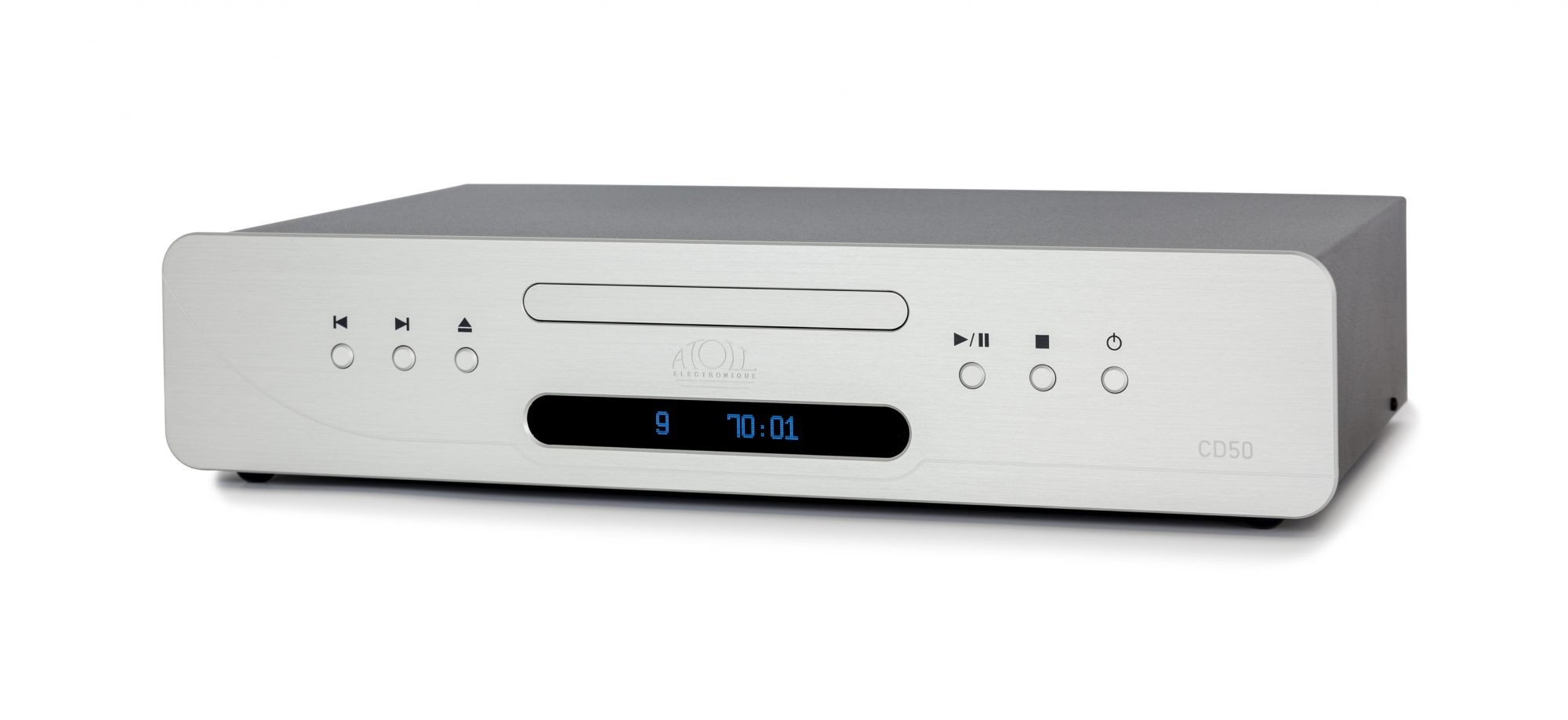
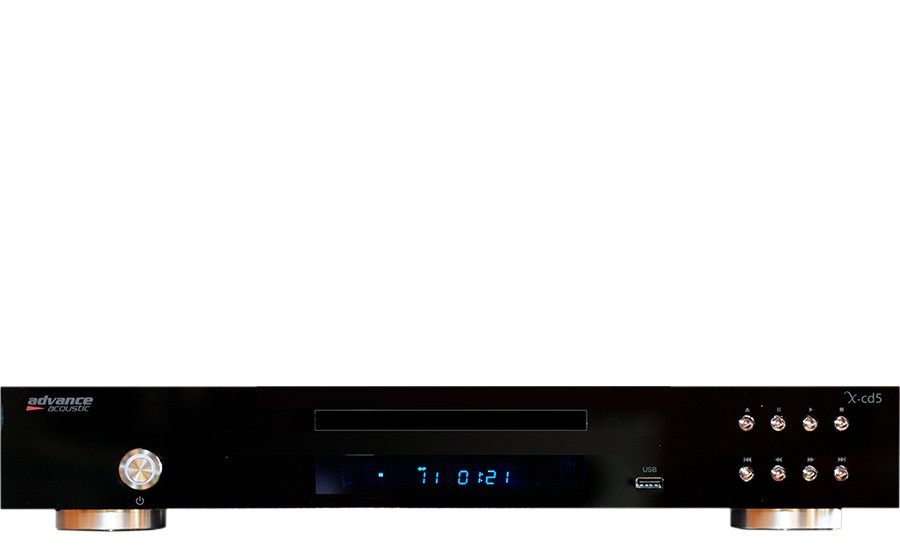
CD Player
Find the perfect CD player to enjoy your CD collection in exceptional sound quality.
These hi-fi devices are designed to get the most out of your record collection, and connect to a pair of active speakers via their line output, or for use with dedicated equipment such as integrated amplifiers and passive speaker pairs.